Measured values differ greatly depending on the leakage current meter’s measurement range.
If the current being measured contains a large harmonic component that is greater than or equal to the range, this issue is caused by the instrument’s inability to properly eliminate the harmonic component.
Symptom
When a leakage current meter’s range was changed, the measured values varied significantly between the two ranges.
Ordinarily, changing the range will not result in a significant change in the measured values.
Instrument settings
- Supported models: AC Leakage Clamp Meter CM4001, CM4002, CM4003
- Filter: ON
- Range: Auto or manual
Solution
If you encounter this issue, measure using a larger range.
For example, if the 60.00 mA and 600.0 mA ranges display measured values that differ significantly, the larger range (600.0 mA) will yield the correct measured value.
Detailed explanation
This explanation assumes that a waveform such as the following is being measured using the 60.00 mA and 600.0 mA ranges.
- Leakage current: RMS value of 5 mA, 50 Hz
- Harmonic component: Crest value of 300 mA, 1.5 kHz
- Instrument range setting: 60.00 mA or 600.0 mA
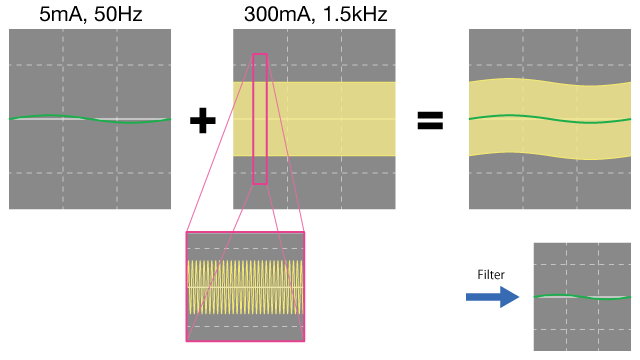
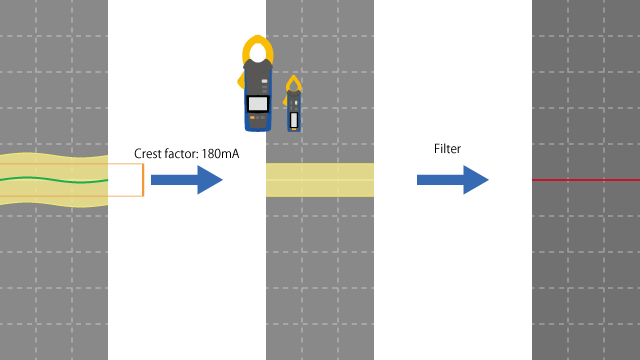
Using the 60.00 mA range
The AC leakage clamp meter’s specifications indicate a crest factor of 3. (See below for more information about crest factor.) This value indicates that the instrument can measure waveforms with a crest value of 180 mA, which is equivalent to 3 times the range. The instrument cannot accurately measure waveforms with a greater crest value.
In this example, the harmonic component crest value is 300 mA, which cannot be measured correctly. The leakage current component will be lost in the instrument’s internal circuitry, as illustrated in the figure below.
Although the harmonic component can be eliminated by applying a filter to the waveform, the leakage current component cannot be captured.
Consequently, a meaningless value close to 0 mA will be displayed as the measured value.
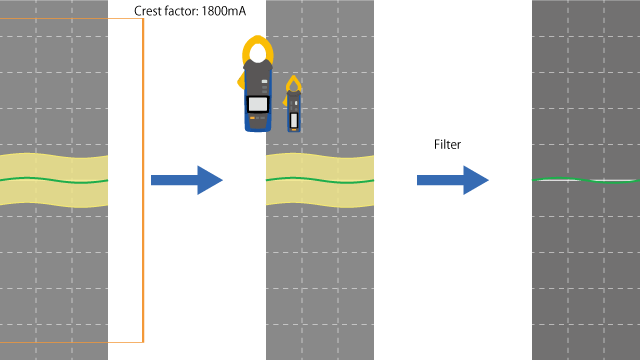
Using the 600.0 mA range
Since the crest factor is 3, the instrument can measure waveforms with a crest value of 1800 mA, which is equivalent to 3 times the range.
Since the harmonic component crest value is 300 mA, it can be measured correctly.
The harmonic component can be eliminated by applying a filter to the waveform, and the leakage current component can be captured.
What is crest factor?
Crest factor, or peak factor, refers to the ratio of the waveform’s RMS value and crest value.
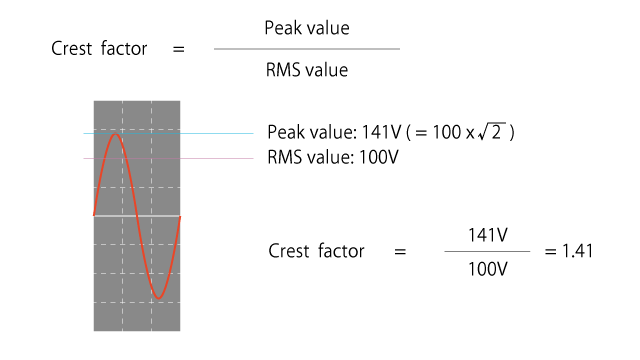
A sine wave has a crest value of 141 V when the RMS value is 100 V, resulting in a crest factor of 1.4.
An instrument’s specifications will define the crest value as the range within which correct measurement is possible for the input terminals.
For example, a voltmeter’s specifications might specify a crest factor of 3 for a 600 V range.
The 600 V range indicates the instrument can measure up to an RMS value of 600 V.
Since the crest factor is 3, the instrument can measure waveforms with an RMS value of 600 V and a crest value of 1800 mA or less, which is equivalent to 3 times 600 V. Since sine waves have a crest factor of 1.4, the instrument can measure a 600 V sine wave.